Hydrogen
At room temperature and pressure, hydrogen gas exists as a diatomic molecule, H2
Occurrence
Hydrogen occurs in water, oils and natural gas
Preparation of hydrogen gas
1 Laboratory preparation of hydrogen
In the laboratory, hydrogen gas can be prepared by reacting:
- a reactive metal with a dilute acid
- a reactive metal with water
Reaction of reactive metal with a dilute acid
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
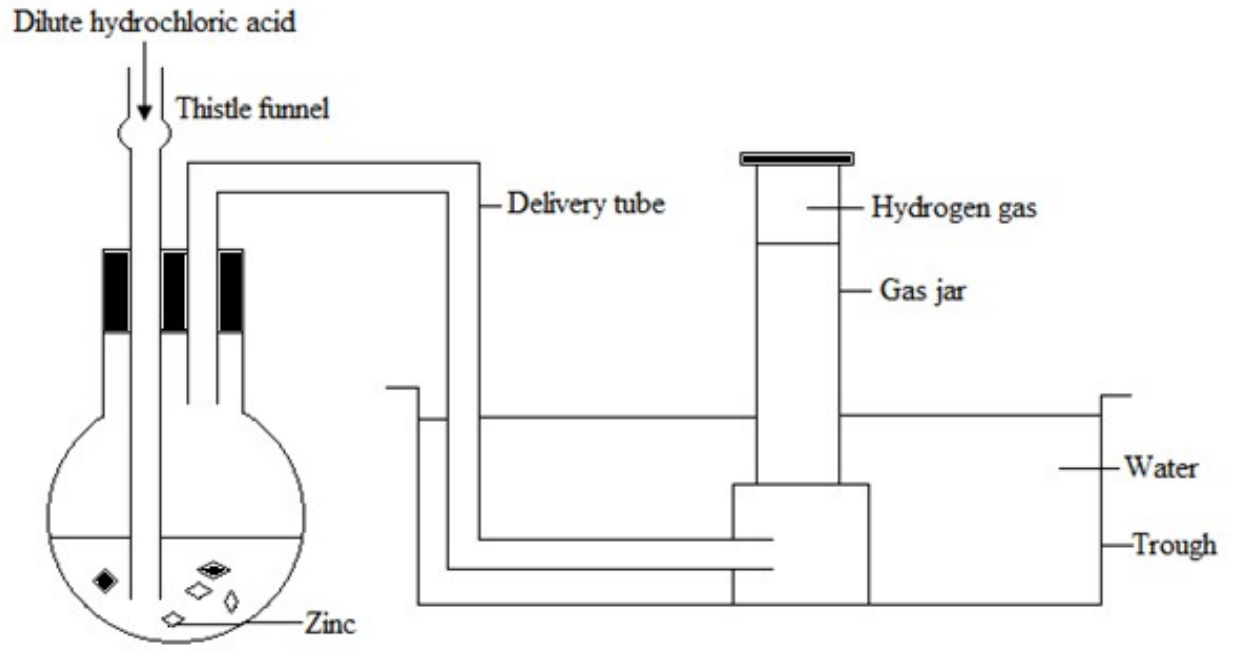
The gas is collected over water
Drying agent: Concentrated Sulphuric acid
Method of collection: Down ward displacement of air or upward delivery since it is less dense
2. Industrial preparation of hydrogen
On the scale, hydrogen gas is manufactured by the reaction of methane and steam
CH4(g) + H2O(g) → CO(g) + 3H2(g)
ConditionsCatalyst: Nickel metal
Temperature: 1000 degree Celsius
Pressure: 50 atmosphere
More steam is then added and the gases are passed over a catalyst iron (III) oxide to remove the carbon monoxide. Carbon dioxide is removed by dissolving it in water under pressure
3. Hydrogen can also be produced by cracking of alkanes
Test for hydrogen
Hydrogen gas burns with a pop sound when a burning splint is introduced to it
Physical properties of hydrogen
- It is colourless
- It is odorless
- It is less dense than air
- It has a boiling point of -253 degree Celsius
- It is not poisonous and does not support life
Chemical properties of hydrogen
- It has no effect on litmus paper
- It burns in oxygen with a blue flame producing a pop sound
- It is a reducing agent. It reduces the oxides of metals below it in the reactivity series. When hydrogen is passed over black copper (II) oxide in the apparatus above, the black powder turns pink
- When hydrogen is passed over black copper (II) oxide in the apparatus above, the black powder turns pink. A mixture of hydrogen and chlorine is explosive in sun light
Uses of hydrogen gas
- It is used in the manufacture of ammonia in haber process
- It is used in the manufacture of margarine from vegetable oil in the process called catalytic hydrogenation
- Liquid hydrogen is used as a fuel in rockets
- It is used as a reducing agent