Angle Properties
Angle Properties is a mathematical concept that deals with angles in relation to each other
« Previous Next »Angle Properties of a Transversal
Below is a diagram showing two parallel line intersected by a line
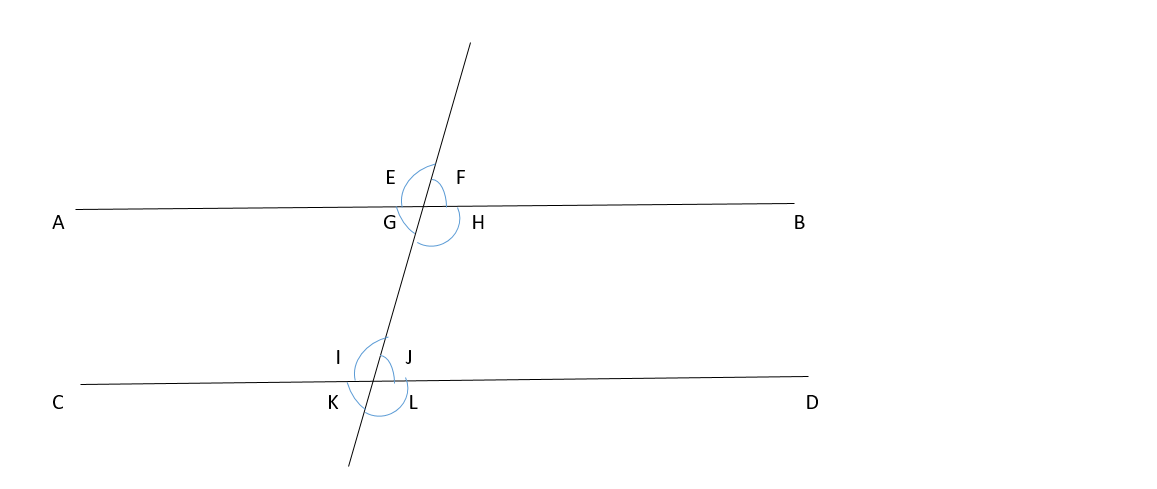
Rules to derive from a Transversal
-
The angle of the straight line adds up to
-
The ange of a circle adds up to
-
Corresponding angles are always equal, from the diagram above the Corresponding angles are:
E = I, F = J, G = K, H = L
-
The sum of Adjacent angles adds up to , example from the diagram above Adjacent angles are:
I + J = , J + L =
-
Alternate angles are equal, examples of alternate angles from the diagram are:
G = J, H = I
-
Vertically opposite angles are equal, from the diagram these kind of angles are:
E = H, F = G, J = K, I = L
-
The sum of interior angles adds up , from our diagram above examples of interior angles are:
G + I = , H + J =
Angle Properties of a Circle
-
Angle at the centre is twice the angle at the circumference standing on the same arc.

-
A right angle triangle in a semi - circle is .

-
Angles subtended in the same segment on a chord of a circle are equal.

-
Opposite angles of a quadrilateral in a circle add up to .

-
Alternate angles made by a tangent which touchs the circle are equal to the segment angles.

Example of circle properties
DE is parallel to CB. Angle ACE = 48°, angle CED = 65° and angle CBE = 73°. Calculate Angle;
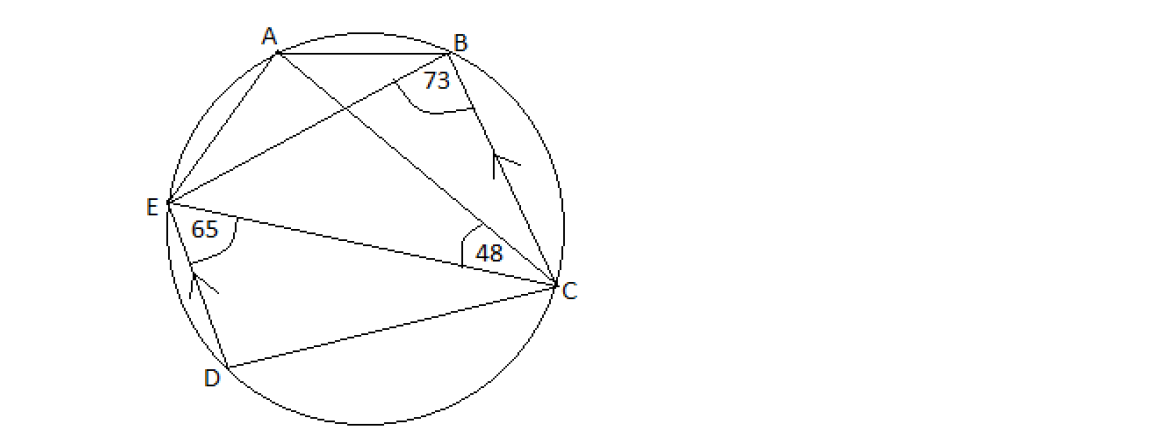
(a) ACB
(b) ABE
(c) BEC
(d) CDE
Solutions:
(a)
From the diagram line DE and CB are parallel, this means that, when you move from D to E to C to B you form a zed (Z). This means that angle DEC and angle ECB are equal because they are alternate angles;
< DEC = < ECB = 65°
We are finding ACB which is part of angle ECB = 65°
In angle ECB = 65° we already have angle ACE = 48°
To find angle ACB we have to subtract ACE from ECB
< ACB = < ECB - < ACE
< ACB = 65° - 48°
Answer: < ACB = 17°
(b)
Look at the diagram, angle ABE is subtended on chord AE, angle ACE is also subtended on the same chord AE. This means that the two angles are equal according to theorem 2 of the previous lesson. Therefore;
< ABE = < ACE = 48°
Answer: < ABE = 48°
(c)
From the diagram, move from B to C to E and back to B, you form a triangle. The rule is that, the sum of three interior angles of a triangle is 180° this means that
< BEC + < ECB + < CBE = 180°
Substitute in the above formula
< BEC + 65° + 73° = 180°
< BEC + 138° = 180°
< BEC = 180° - 138°
Answer: < BEC = 42°
(d)
Look at the diagram; CBE and CDE are opposite angles in a cyclic-quadrilateral. This means that angle CBE and angle CDE add up to 180°
< CDE + < CBE = 180°
Substitute for < CBE = 73°
< CDE + 73° = 180°
< CDE = 180° - 73°
Answer: < CDE = 107°
How to solve circle properties
In the diagram below, A, B, C, and D lie on the circumference of the circle, centre O.
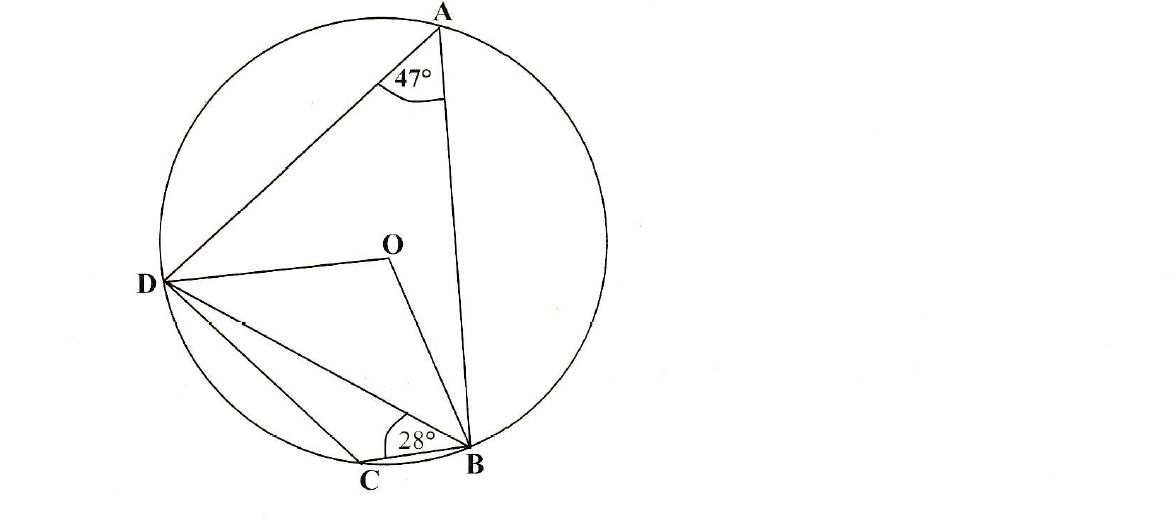
Given that BAD = and DBC = ,
Calculate
a) BOD
b) OBD
c) BDC
Solution
a) To find Angle BOD , you need to apply the angle property that states that angle at the centre is twice the angle at the circumference standing on the same arc
BOD = 2( BAD)
BOD = 2( 47)
Answers: BOD =
b) OBD is an isosceles triangle meaning that it has two equal sides and angles because the lines OB and OD are equal and joining at the center on a cricle
BOD = and having in mind that a triangle add up to
OBD = (180 - BOD) / 2
OBD = (180 - 94) / 2
Answers: OBD =
c) To find angle BDC, apply the quadrilateral angle property which states that the opposite angles adds up to
Therefore BCD = 180 - 47
BCD = , after finding angle BCD add it with and then subtract the sum of a triangle which is
BDC = 180 - 133 + 28
Answers: BDC =